Computer Numerical Control (CNC) programming is the backbone of modern manufacturing. At its heart lie the G and M codes, fundamental programming languages that enable CNC machines to perform precise and complex tasks. This article explores the vital role G and M codes play in CNC programming and their significance in optimizing machining processes.
Understanding G and M Codes: The Language of CNC Machines
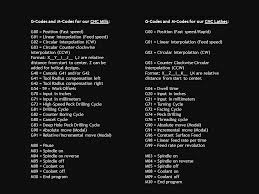
G and M codes serve as the core communication tools between the programmer and the CNC machine. G codes, or geometric codes, direct the machine on how to move—whether it’s linear or circular interpolation, rapid positioning, or tool paths. For instance, commands like G01 indicate linear cutting, while G02 and G03 define circular movements in clockwise and counterclockwise directions, respectively. These instructions form the foundation of a program, guiding the machine to carve or shape materials with high precision.
M codes, or miscellaneous codes, control auxiliary functions like spindle speed, coolant flow, and tool changes. Commands like M03 (spindle on clockwise) and M08 (coolant on) provide operational support that complements the machine’s geometric tasks. Together, G and M codes create a symbiotic system where precision and functionality work in harmony to achieve desired machining outcomes.
Enhancing Precision and Efficiency in Machining
The precision offered by G and M codes is unparalleled, allowing manufacturers to produce parts with tolerances as tight as micrometers. G codes ensure that tool paths are meticulously followed, reducing errors caused by human intervention. The exact positioning and motion control enable the production of intricate components, such as those required in aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
Efficiency is another hallmark of using G and M codes. These codes optimize machining cycles by eliminating redundant steps and automating processes like tool changes or spindle adjustments. M codes, for example, ensure seamless transitions between operations, saving time and reducing machine downtime. This combination of precision and efficiency makes G and M codes indispensable in modern CNC programming.
The Role of G and M Codes in Customization and Flexibility
G and M codes empower manufacturers to customize machining processes for specific needs. A programmer can tailor the toolpath and operation sequence to accommodate unique design specifications or material properties. This flexibility is particularly important when working with diverse materials like metals, plastics, and composites, each requiring distinct cutting parameters and strategies.
Moreover, the adaptability of G and M codes enables the creation of prototypes and small production runs without extensive retooling or setup changes. By modifying the code, manufacturers can seamlessly switch from one design to another, ensuring responsiveness to market demands and customer requirements. This level of customization underscores the versatility of G and M codes in CNC programming.
Simplifying Complex Operations with G and M Codes
Complex machining operations, such as 5-axis machining or multi-tool setups, rely heavily on the clarity and structure of G and M codes. These codes simplify intricate processes by breaking them into manageable instructions. For example, a G43 command activates tool length compensation, essential for maintaining consistent depth during multi-axis operations.
Additionally, M codes streamline auxiliary tasks, like coolant management (M08/M09) and spindle orientation (M19), ensuring that complex setups operate smoothly. The ability to program these functions ensures that even the most sophisticated operations are executed with precision and minimal manual intervention, making G and M codes vital for advanced manufacturing applications.
The Future of G and M Codes in CNC Programming
As CNC technology evolves, the role of G and M codes continues to grow. The integration of CAD/CAM software with CNC programming has enhanced the accessibility and efficiency of creating G and M code sequences. Modern software generates these codes automatically, translating complex 3D models into machine-readable instructions while maintaining the precision and reliability of traditional manual programming.
Looking ahead, advancements like adaptive machining and smart manufacturing will further elevate the importance of G and M codes. These codes will integrate with AI and IoT technologies, enabling real-time adjustments and predictive maintenance in CNC operations. While the language of G and M codes may evolve, their foundational principles will remain a cornerstone of CNC programming, ensuring continued innovation in the manufacturing sector.
Conclusion
G and M codes are more than just programming instructions—they are the lifeblood of CNC machining. Their role in enabling precision, efficiency, customization, and the execution of complex operations is unparalleled in the manufacturing industry. As technology advances, the importance of G and M codes will only increase, solidifying their place as essential tools in shaping the future of CNC programming and modern manufacturing.



Leave a Reply