Introduction
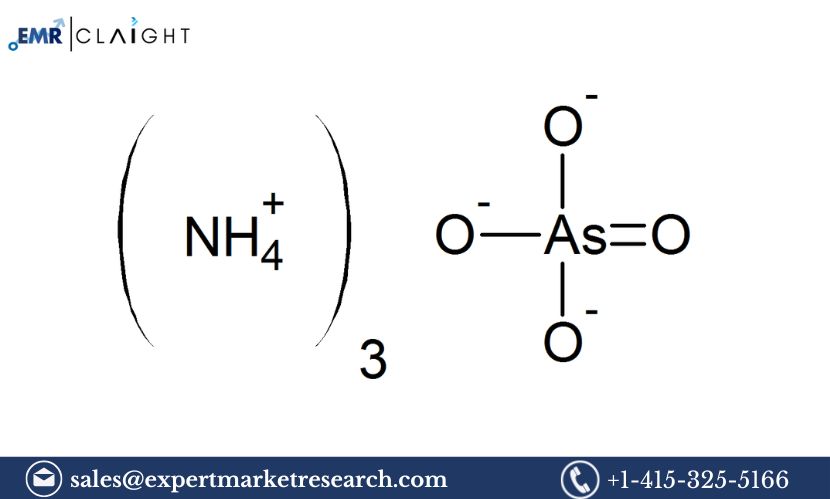
The Ammonium Arsenite Manufacturing Plant Project Report provides a comprehensive analysis and planning guide for establishing a plant that produces ammonium arsenite, a chemical compound widely used in various industrial applications. Ammonium arsenite, also known as arsenic trihydride or arsenic acid ammonium salt, plays a crucial role in sectors such as pest control, wood preservation, and as a reagent in laboratories. It is a compound with a strong toxicological profile, requiring careful handling and adherence to environmental and safety regulations during manufacturing.
The purpose of this report is to outline the steps involved in setting up a manufacturing facility for ammonium arsenite. The report covers all aspects, from market demand, raw material sourcing, manufacturing processes, plant layout, and equipment to financial considerations, environmental impact, and regulatory compliance. Understanding these factors is essential for anyone considering an investment in the ammonium arsenite production industry.
Industry Overview
Ammonium arsenite is primarily used in the manufacturing of pesticides, herbicides, and fungicides due to its ability to control pests effectively. It is also used in the preservation of wood products, acting as a fungicide and insecticide, which prolongs the life of the treated materials. Despite its toxicity, ammonium arsenite has found continued use in various industrial processes due to its effectiveness.
The chemical is generally produced in controlled environments, and safety measures are paramount due to its hazardous nature. The demand for ammonium arsenite is concentrated in agricultural sectors, particularly in countries with large agricultural outputs and significant pest control needs. It is also used in niche industrial applications such as mining for its ability to dissolve metals and in certain laboratory applications as a reagent.
Applications of Ammonium Arsenite:
- Pesticides and Herbicides: Used for controlling pests in agriculture, particularly in rice, cotton, and vegetable farming.
- Wood Preservation: Acts as a preservative against fungi and insects.
- Industrial and Laboratory Use: Employed as a reagent in various chemical processes and laboratory procedures, such as in the preparation of arsenic compounds.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Market Demand and Growth Potential
The market for ammonium arsenite is directly linked to its industrial and agricultural applications. Given the increasing demand for pesticides and herbicides in global agriculture, as well as the rise in pest-related challenges, the need for ammonium arsenite continues to rise. According to market analysis, the global pesticide market is projected to grow at a steady rate, with certain regions such as North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific witnessing significant growth in demand for ammonium arsenite.
Factors driving this demand include:
- Agricultural Expansion: The growing need for food production and pest management solutions in both developed and developing countries is a key driver of ammonium arsenite usage in agriculture.
- Increased Awareness of Wood Preservation Needs: As the demand for durable and long-lasting wood products increases, the need for ammonium arsenite-based wood preservatives is also expected to rise.
- Niche Industrial Demand: Ammonium arsenite’s specific applications in laboratories and its ability to dissolve metals in certain industrial processes maintain its niche demand.
Raw Materials and Supply Chain
The primary raw materials required for the production of ammonium arsenite are arsenic oxide (As2O3), ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), and water. These chemicals must be sourced from reliable suppliers to ensure consistent production quality.
Key Raw Materials:
-
Arsenic Oxide (As2O3): This is the source of arsenic, which is a key component in the production of ammonium arsenite. Arsenic oxide is typically derived from the roasting of arsenic-containing ores.
-
Ammonium Hydroxide (NH4OH): A solution of ammonia in water, ammonium hydroxide is used to combine with arsenic oxide in the manufacturing process to form ammonium arsenite.
-
Water: Used as a solvent in the production process to ensure the proper consistency and reaction between the chemicals.
Supply Chain Considerations:
- Sourcing Arsenic Oxide: The procurement of arsenic oxide is critical, as its quality directly impacts the final product. Given the toxic nature of arsenic, suppliers must adhere to safety and environmental regulations.
- Transportation and Storage: Due to the hazardous nature of arsenic and ammonia, the transportation and storage of these materials require special safety measures and regulatory compliance.
- Supplier Relationships: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers of raw materials ensures timely deliveries and consistency in the production process.
Manufacturing Process
The production of ammonium arsenite involves a chemical reaction between arsenic oxide and ammonium hydroxide in a controlled environment. The process must be carried out with extreme care, as the chemicals involved are highly toxic and pose significant risks to health and the environment.
Steps in the Manufacturing Process:
-
Preparation of Raw Materials: Arsenic oxide is weighed and mixed with ammonium hydroxide in a carefully controlled ratio. Ammonium hydroxide must be added slowly to avoid excessive heat generation, which could cause dangerous reactions.
-
Separation and Filtration: After the reaction, the mixture is filtered to separate the ammonium arsenite from any unreacted materials or by-products. The remaining liquid or slurry is discarded safely according to hazardous waste disposal regulations.
-
Drying: The ammonium arsenite is then dried in a controlled environment to remove excess moisture. The drying process helps to stabilize the compound and prepare it for packaging.
-
Quality Control and Testing: The dried ammonium arsenite is subjected to rigorous quality control measures, including purity tests and toxicological evaluations, to ensure that it meets the required standards for industrial use.
-
Packaging: Once the ammonium arsenite passes quality control, it is packaged in sealed containers, ensuring that it is protected from contamination and degradation. Specialized containers are used to prevent exposure to air and moisture, as this can affect the chemical properties of the compound.
Plant Layout and Equipment
Setting up an ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant requires specialized equipment and careful consideration of plant layout to ensure safety and efficiency.
Essential Equipment:
-
Reactor Vessels: These are used for the reaction between arsenic oxide and ammonium hydroxide. The reactors must be equipped with temperature and pressure control mechanisms to prevent accidents.
-
Filtration Units: Used for separating the ammonium arsenite from unreacted materials after the reaction.
-
Drying Units: The drying units help to remove excess moisture from the ammonium arsenite to create a stable, fine powder or crystalline product.
-
Packaging Machines: Specialized packaging machinery is necessary to pack the ammonium arsenite in sealed containers to prevent exposure to harmful substances and ensure safety during transport.
-
Safety Equipment: Given the toxic nature of the chemicals involved, personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, masks, and goggles, as well as safety hoods and ventilation systems, are essential for worker safety.
Plant Layout Considerations:
- Separation of Processes: The plant should be divided into distinct areas for each step of the manufacturing process, such as raw material storage, reaction vessels, filtration units, and drying areas. This helps in minimizing cross-contamination and managing risks.
- Ventilation and Hazard Control: Given the toxic nature of arsenic and ammonia, the plant must be equipped with effective ventilation systems, exhaust fans, and air filtration to protect workers from exposure.
- Waste Disposal Area: A designated area should be allocated for the safe disposal of chemical waste, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations.
Financial Considerations
Establishing an ammonium arsenite manufacturing plant requires substantial capital investment. The primary costs include land acquisition, plant construction, procurement of equipment, raw materials, and operational expenses.
Key Financial Components:
-
Capital Expenditure (CapEx):
- Investment in land, buildings, and infrastructure
- Purchase and installation of equipment, including reactors, filtration systems, and dryers
- Setup of safety systems and environmental control measures
-
Operating Expenses (OpEx):
- Raw material procurement (arsenic oxide and ammonium hydroxide)
- Labor costs for plant workers and technicians
- Utility costs for water, electricity, and waste management
- Maintenance of equipment and machinery
-
Revenue Projections: Revenue will depend on factors such as production capacity, market demand, and pricing strategies. The price of ammonium arsenite is influenced by its application in various industries, particularly in agriculture and wood preservation.
-
Return on Investment (ROI): A break-even analysis can help determine when the initial investment will be recouped and when the plant will start generating profits.
Environmental and Safety Regulations
Ammonium arsenite is a hazardous chemical, and its production must comply with stringent environmental and safety regulations. These regulations include the proper handling, storage, and disposal of chemicals, as well as measures to ensure worker safety.
Key Considerations:
- Waste Disposal: All by-products and chemical waste must be disposed of in compliance with local and international environmental regulations. This includes the safe disposal of arsenic-contaminated materials.
- Worker Safety: The plant must implement a robust safety program, including personal protective equipment (PPE), emergency response procedures, and regular training for employees.
- Regulatory Approvals: The plant must obtain the necessary permits and certifications to operate legally, including those related to environmental impact, health and safety, and chemical production.
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Peter Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au




Leave a Reply